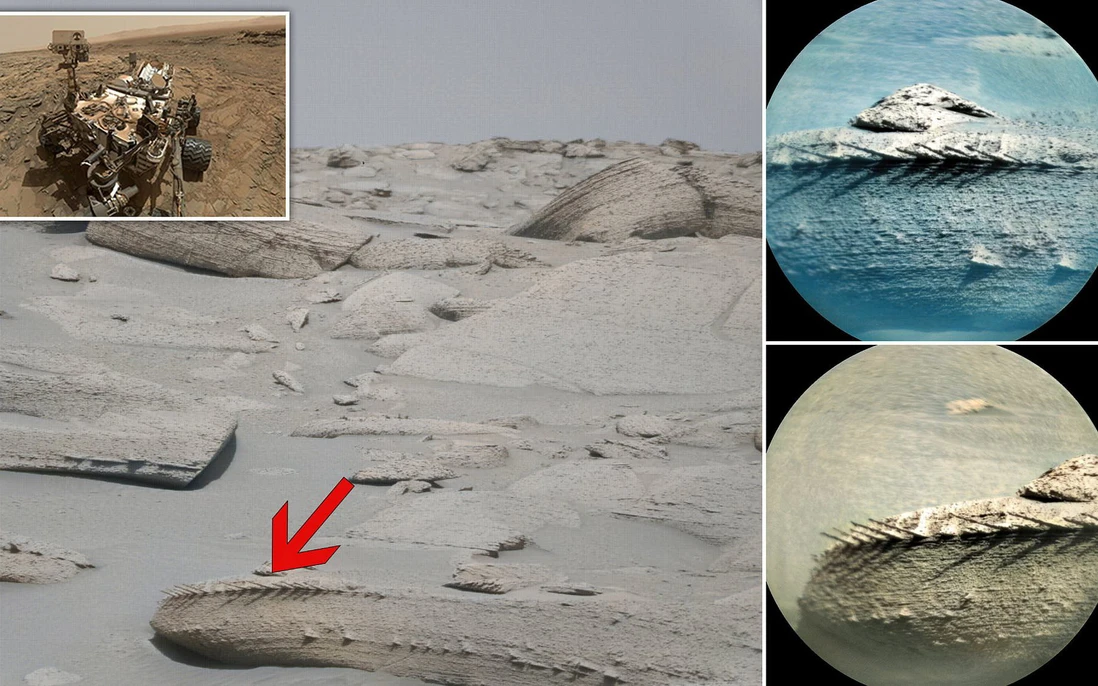
NASA has made a groundbreaking discovery on Mars that could reshape our understanding of the Red Planet’s history. Recently, the Perseverance rover, part of NASA’s Mars exploration mission, identified rocks on the Martian surface resembling fossilized bones. This exciting discovery has sparked new hope among scientists that ancient life may have once existed on Mars.

### Discovery of Fossil-Like Bone Rocks on Mars
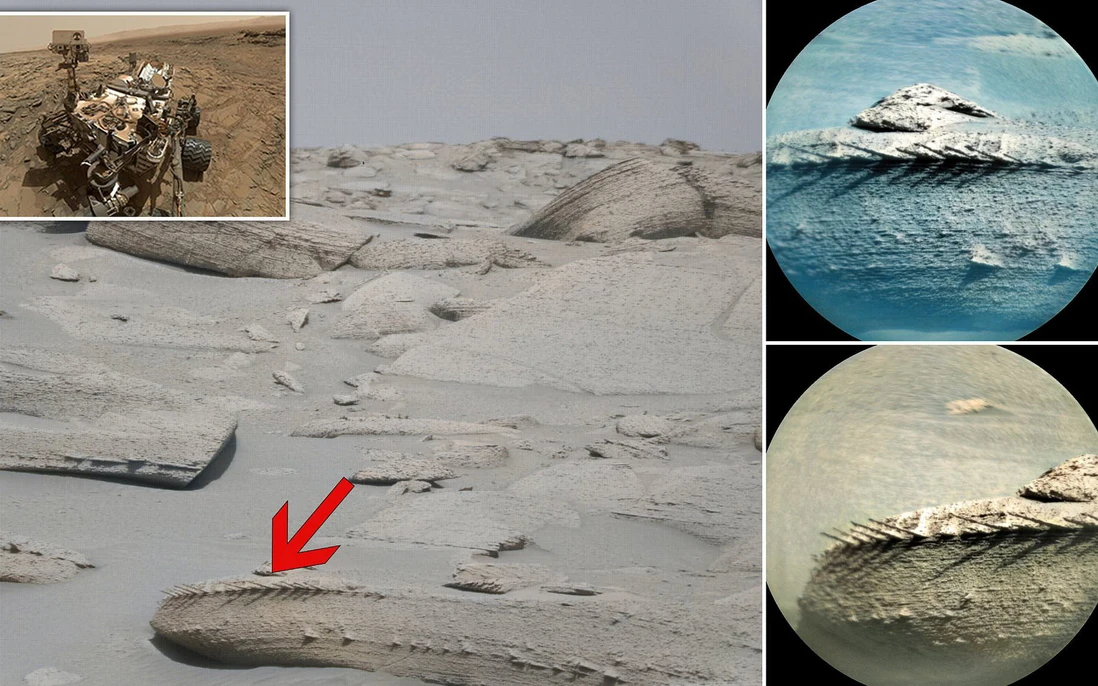
The Perseverance rover, which has been exploring the Jezero Crater since it landed on Mars in 2021, made this remarkable find while surveying the Martian landscape. Jezero Crater, a region once believed to have housed a lake billions of years ago, has long been a prime location for studying signs of ancient life. During its explorations, Perseverance captured images and collected data from rock formations that bear a striking resemblance to fossilized bones found on Earth. These fossil-like structures have raised intriguing possibilities, as they hint at the presence of biological activity that could have occurred in Mars’ distant past.
### What Makes This Discovery Significant?
This discovery holds profound implications not only for planetary geology but also for the ongoing search for extraterrestrial life. The bone-like appearance of these rocks has led scientists to consider the possibility that Mars might have once harbored life forms, potentially microbial, that left traces in the planet’s rocky terrain. If these rocks are indeed fossil remnants of ancient Martian organisms, it would be one of the most significant scientific breakthroughs in history, offering compelling evidence that life once thrived beyond Earth.

### The Search for Life on Mars Takes a New Step Forward
NASA has long been at the forefront of the quest to determine whether Mars, now a barren and inhospitable world, once supported life. This latest discovery adds weight to the hypothesis that Mars’ early history may have included favorable conditions for life to develop. By analyzing the geological features of Mars, scientists aim to uncover whether the Red Planet ever had the right combination of water, organic molecules, and stable environments to sustain life.
While the bone-like rocks are an exciting lead, scientists remain cautious. Further analysis is required to determine if these formations are indeed of biological origin or if their resemblance to fossilized bones is purely coincidental, resulting from Mars’ unique geological processes. Perseverance will continue its mission, collecting samples from these rock formations, which may one day be returned to Earth for closer study. The results of these analyses could provide critical insights into the mystery of Mars’ past.
### Jezero Crater: A Key Location for Ancient Life Exploration
The Jezero Crater is a particularly promising site for these investigations. Billions of years ago, this crater housed a large lake and river delta, where water once flowed freely—a critical ingredient for life as we know it. NASA selected Jezero Crater as Perseverance’s landing site specifically because of the strong potential to uncover signs of past life. Scientists believe that if life ever existed on Mars, it may have thrived in environments like this ancient lake, where water and minerals created a habitat potentially suitable for microorganisms.
This latest discovery of fossil-like rocks is especially intriguing because it aligns with previous evidence suggesting that Mars had liquid water and potentially habitable conditions in its ancient past. If confirmed, it could bolster the argument that Mars was once home to living organisms, perhaps during a time when Earth’s early life forms were also emerging.
### Implications for Future Mars Missions
This discovery represents an important step forward in understanding Mars’ potential to host life. As NASA continues to study these rock formations, other planned missions aim to further explore Mars and eventually bring samples back to Earth for detailed analysis. The upcoming Mars Sample Return (MSR) mission, a collaboration between NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA), will play a critical role in this effort. Scheduled for launch in the late 2020s, MSR will retrieve and return samples that could definitively determine the biological nature of the fossil-like rocks discovered by Perseverance.
The discovery also sparks renewed interest in future crewed missions to Mars. While robotic missions like Perseverance are invaluable for gathering data, human explorers could provide more nuanced insights into the planet’s geology and search for evidence of life. NASA’s Artemis program, which aims to land humans on the Moon by 2025, could eventually lead to crewed Mars missions, allowing scientists to directly investigate key locations like Jezero Crater.
### Could Mars Have Once Harbored Life?
Mars has long been a focal point for scientific inquiry regarding the possibility of extraterrestrial life. The planet’s climate today is cold, dry, and hostile to life as we know it, but evidence of ancient riverbeds, lakes, and now potential fossil-like formations suggest that conditions may have been very different in Mars’ distant past. For decades, planetary scientists have speculated that Mars, much like early Earth, might have had the right conditions for microbial life to emerge. This recent discovery could be a crucial piece of that puzzle.
However, caution is key. The resemblance of these rocks to fossilized bones is just the beginning of a much longer investigative process. Researchers will need to examine not just the morphology of these rocks but also their chemical composition, structure, and surrounding environment to determine whether they are truly biological in origin.
The discovery of fossil-like bone rocks on Mars is a major milestone in our quest to uncover the mysteries of the Red Planet. Whether these rock formations turn out to be actual fossils or simply a product of geological processes, this finding is a significant step toward answering the age-old question: Are we alone in the universe? As NASA continues its mission to explore Mars, the potential to unlock evidence of ancient life grows closer with each new discovery.
In the coming years, as more data is gathered and samples are analyzed, we may finally gain a clearer picture of Mars’ fascinating history—and perhaps, the origins of life itself.

