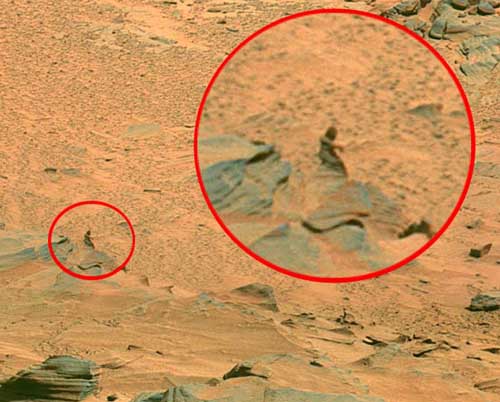
In a groundbreaking revelation, NASA’s ongoing exploration of the Red Planet has unearthed a startling discovery—a rock on the surface of Mars bearing an uncanny resemblance to a fossilized bone. This unexpected finding has sent shockwaves through the scientific community and reignited speculation about the potential for ancient life on Mars. Join us as we delve into NASA’s discovery of this bone-like rock and its implications for our understanding of Martian geology and astrobiology.

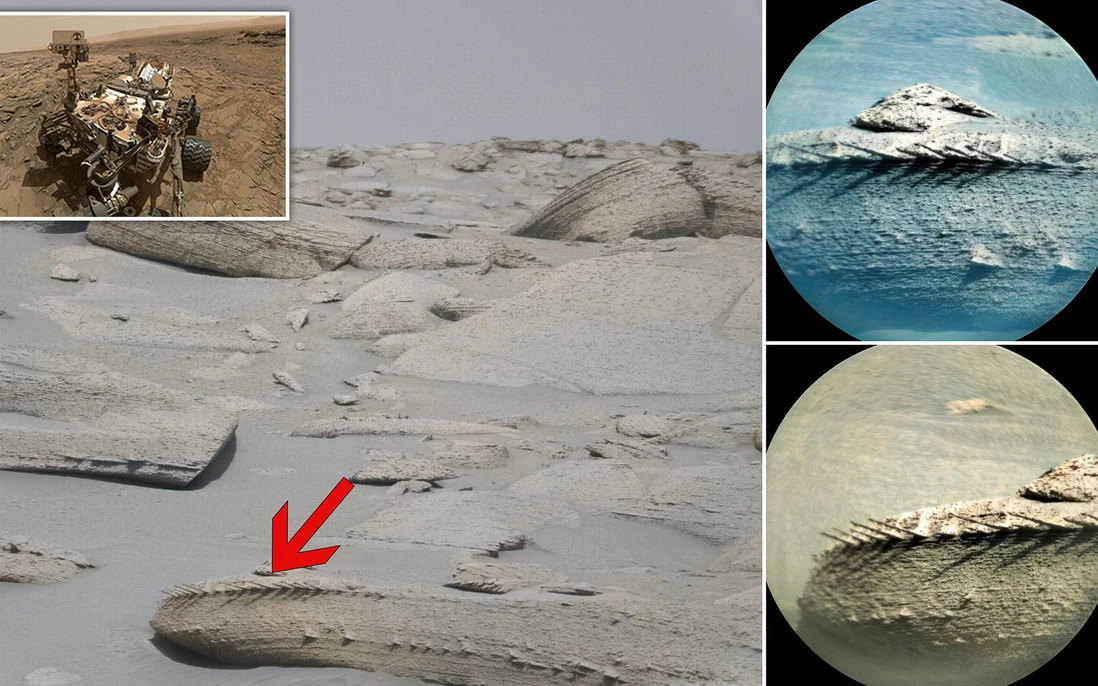
The Discovery Unveiled: Amidst the rugged terrain of Mars, NASA’s Curiosity rover, equipped with advanced instruments and cameras, diligently explores the Martian landscape, capturing images that reveal the planet’s secrets. Amongst the rocky outcrops and dusty plains, one particular formation stands out—a rock formation resembling the shape and texture of a long-degraded bone. This serendipitous discovery has sparked intense interest and debate among scientists and enthusiasts alike.
Interpreting the Evidence: As images of the bone-like rock circulate within scientific circles, experts analyze the geological characteristics and context of the formation to determine its origins. While some researchers caution against premature conclusions, citing the possibility of geological processes mimicking organic shapes, others speculate that the rock may indeed be a remnant of ancient life on Mars. The debate underscores the complexity of interpreting Martian geology and the need for further investigation.

Implications for Astrobiology: The discovery of a bone-like rock on Mars holds profound implications for the field of astrobiology—the study of life beyond Earth. If confirmed as a fossilized bone, this finding would provide compelling evidence of past life on the Red Planet, raising questions about the potential for habitability and the origins of life in the cosmos. Moreover, it would fuel excitement about the prospect of future missions to search for signs of ancient life on Mars.
Challenges and Skepticism: Despite the excitement surrounding the discovery, skepticism abounds within the scientific community, as researchers grapple with the inherent challenges of studying Martian geology from afar. The harsh Martian environment, coupled with the limitations of remote sensing technologies, complicates efforts to conclusively identify the nature of the bone-like rock. Nevertheless, scientists remain undeterred in their quest to unlock the mysteries of Mars.
Future Exploration: In the wake of this remarkable discovery, NASA and other space agencies are redoubling their efforts to explore Mars and search for evidence of past or present life. Planned missions, including the Mars Sample Return mission, aim to collect and analyze rock samples from the Martian surface, providing unprecedented insights into the planet’s history and potential for habitability. With each new discovery, humanity edges closer to unraveling the enigma of Mars and our place in the universe.
NASA’s discovery of a bone-like rock on the surface of Mars marks a significant milestone in our quest to understand the Red Planet and the possibility of life beyond Earth. While the true nature of the formation remains a subject of debate, its implications for astrobiology and future exploration are profound. As we continue to explore the mysteries of Mars and the cosmos, each new revelation brings us closer to answering age-old questions about the nature of life and the universe.

